Data scraping is an activity on the verge of law, which has its own features and nuances. And if one day you wake up and realize that it’s time to get a bunch of fresh data, then it’s time to understand how legitimate this action is. The legality of data scraping it’s a basic thing you should know before scraping.
Data scraping is a service that has become very popular in recent years. 🚀People need a lot of information to solve a lot of problems. Some of this information cannot be obtained manually.
Look at how the volume of the data scraping market increases year by year. This service inevitably and rapidly enters our lives.
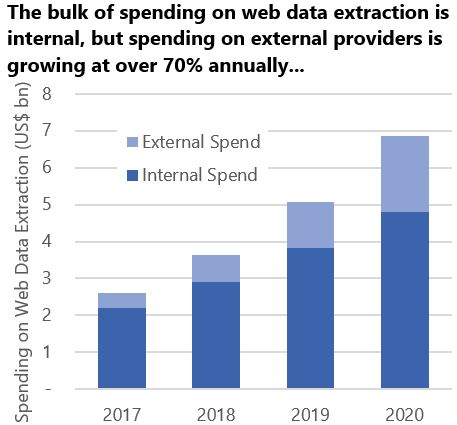
Google knows for sure that there are at least 20 big companies fighting for this segment of the market. But no matter how beautiful and conceived the website of such companies. We could not find much information about the legality of web scrapers. And we would like to correct this gap to the best of our abilities. 🧙
First of all, we want to note that the story below is our personal opinion. It is reasoning which is based on our experience and our vision of the market. We are not good lawyers, and we believe that the law may be interpreted in different ways. However, we believe that you may be interested to know our position. So, let’s go!
A little bit about the laws
The field of data extraction is very young. Many countries so far do not have laws that directly regulate data scraping. Typically, automatic data collection is governed by laws that generally apply to computer technology. However, by using scraping, you should be clear about how it complies with the laws of the country in which you are located.
If we are talking about data scraping within the U.S., we may point to the following law that may apply in this matter: https://codes.findlaw.com/us/title-18-crimes-and-criminal-procedure/18-usc-sect-1030.html
We strongly recommend that you use scraping according to the laws of the country in which you are located.
What is an internet site?
An Internet site is a collection of textual data and images that are available to the public. When a company creates a website, it accepts that the information on the website will be available to an unlimited number of people. Even if the site implies a login and password.
The publicity of websites is a fairly obvious thing. The Internet is intended for distribution of the information. Any company pursues the purpose of maximum distribution of the information about itself by means of the Internet site. Will you try to argue with this statement?
So, any site on the Internet is available to an undefined circle of people. Does it mean that a certain person can take some information and save it? Logical example – you browse the site with ads and rewrite phone numbers on a sticker. Is it legal? Does the owner of the message board know that you can do it? Can he be against such an activity?
Humans vs robots issue
Let’s say you have a small business – you sell chessboards. You know that there are at least 3 such shops in the city where the same boards sell your competitors. You, as an experienced businessman, go to these shops once a month or send your acquaintance there to look at the prices and compare them with your prices. Is it legal? Yes, it is. Is there any chance that your competitors will call the police the next time you come to them? We don’t think so.
Now let’s get back to reality. A reality in which we no longer walk around shopping, but use websites to buy and sell products. What do we do in business? We check competitors’ prices through websites, do market analysis, and collect statistics. Often, and especially at the beginning of the business, we do it with our own hands, or do it with the hands of our colleagues. And as you will probably agree, we are not afraid that lawyers from competitors will come to our office and threaten us in court.
And now let’s turn to automating this process. The application to automate the collection of competitors’ prices is simply an application that replaces human labor. So why does human labor remain legal and acceptable and the application may raise questions?

You will be surprised, but many well-known companies actively use such methods. Applications for automatic price comparison are often used in large businesses.
The mystery of hammer manufacturers
Well – a lot of companies around the world produce hammers. We think it’s a very handy device for nailing. But the hammer is basically a double thing. We think almost any hammer can be used for both good and evil. And yet, it doesn’t occur to anyone to sue these manufacturers, does it? To sue a hammer maker because some person has used a hammer to rob someone.
It’s equally absurd to assume that one day the police will break into your house and confiscate your hammer. They’ll take it away because they say it’s too dangerous to be kept by a common man.
But why, when we’re talking about hammers, it’s very clear and absurd to everyone. And when we talk about applications, do we allow some fear or uncertainty in our judgment? That the hammer is the application. These things are tools in their own right. It’s up to you whether you use them properly, for their intended purpose or skillfully.
Legality of text information scraping
Text extraction is one of the classic types of information scraping. It can be descriptions of goods or services, popular science articles, some technical information or anything else. In any case, when you extract text information, the legitimacy of this process will largely depend on the goals you pursue.
The most common type of data scraping is extracting a description from product cards for later use on your website. For example, a certain manufacturer produces phones. Each phone has its own unique description and characteristics. In this case, from description to description, the characteristics and parameters of the products do not change. When you extract such descriptions, you simply create another take of the technical information. It’s like rewriting this information from a product manual. In this case, it is very likely that such data scraping will not be a legal problem.
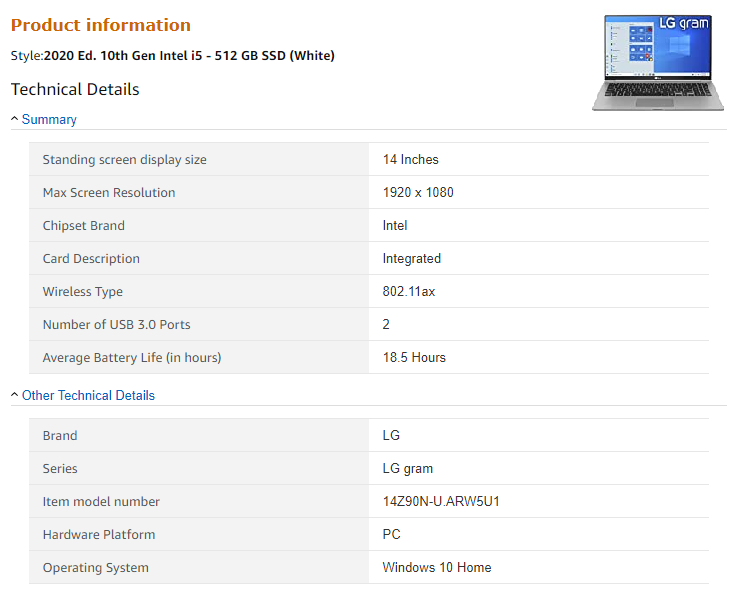
Here is a good example of a classic text with technical specifications. Such text can be found on every site where this notebook is sold. Do you think it’s legal? Will any of the sites fight for the copyright of such information?
On the other hand, sometimes there are situations when a text with a certain copyright and explicit authorship is extracted from a site. Such cases may include author’s reviews of various goods or devices, technical or art articles, news sketches. When scraping and subsequent use of the original texts with such copyright, you are likely to face legal problems.
Legality of scraping pictures
When we talk about scraping pictures, the situation here is a little more complicated. In recent decades, the legal framework has evolved to protect the copyright of images and other results of artistic creation. All pictures from the Internet, as well as all pictures in real life, are the results of the creativity of some people. And even if there is no copyright on an image, it does not mean that it emerged out of nowhere – by itself.
An example of a site that clearly shows the concept of authorship – shutterstock. Here you can buy and sell photos and other images.
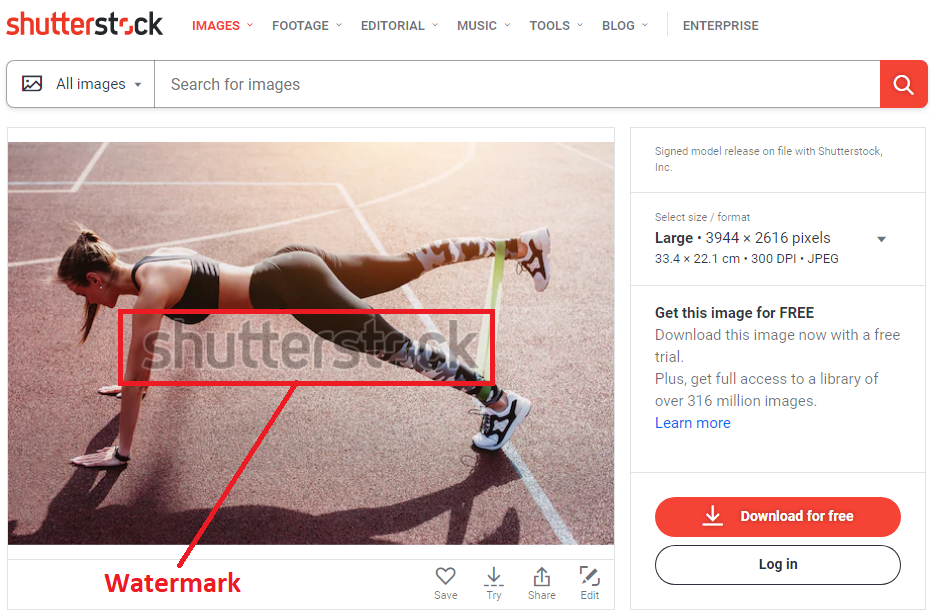
Technically, directly scraping pictures isn’t illegal. You may well collect this data for your internal needs. Problems with the legal framework arise from the moment you decide to publish these scraped pictures on your site. From the moment you publish it, technically speaking, you are a copyright infringer. And even if you have an oral agreement to do so, without written consent in most cases you will be in a vulnerable position.
Of course, there are many situations in which scraping and subsequent use of pictures is not something wrong based on common sense. For example, your supplier can not directly provide a price list with pictures. But he may be interested in your website to increase the volume of purchases. In such case he may allow you to use information from his site.
On the other hand, it should be remembered that scraping images with subsequent use is often a violation of copyright. It is especially relevant in cases where the copyright is directly depicted in the pictures. Yes, this actually means that the author of the photo has put his signature under the photo, and he may not want the photo to be used by someone else.
User Agreement and its features
Almost every site has its own rules of use. Sometimes this information is located in the contract-offer. Sometimes you can find this data in the user agreement. In any case, almost any site has such a section. The legality of data scraping directly depends on the user agreement of the site.
Often, such rules give the position of the site owners on how they relate to automated data collection. This may be stated explicitly (for example – automated data collection is prohibited), or in a conservative way (for example – it is prohibited to copy data from the site). In any case, almost all agreements have such notices.
If you have found a section of the user agreement on the site, and if you have found the relevant prohibitions – well, the site does legally limit you. In such a situation, if the site owners can prove your scraping activity – probably they can win the dispute in court if it happens.
For example, Facebook expressly prohibits in its rules the use of automation tools for data collection. Thus, by extracting data from the Facebook site with the help of scraper, you are potentially in a vulnerable position.
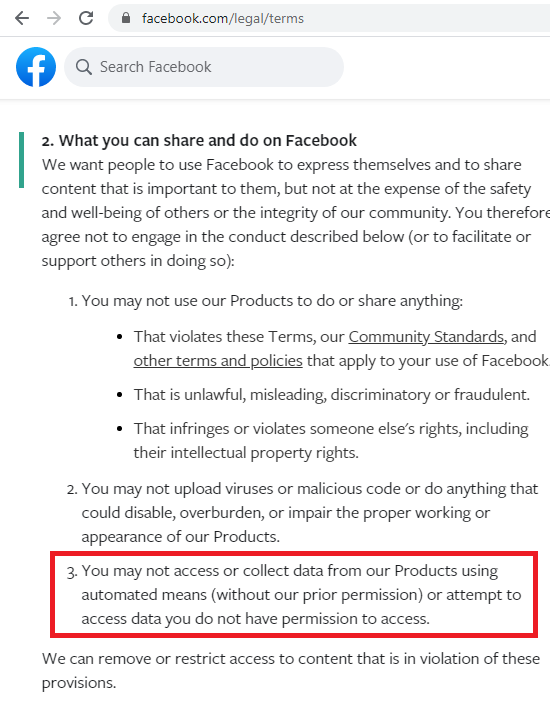
Here we return to the interpretation of the legal framework and judicial practice. The legality of the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the user agreement depends greatly on the purpose for which you collect data from the site. In one case, it may be legal, but in another case, it may not. In one case, the User Agreement may actually limit you, and in another case, it may simply be an inscription that does not comply with the legal framework of the your country and does not limit you in your activities.
Legality of data scraping – conclusion
Data scraping is currently ambiguous from a legal point of view. This market is just beginning to appear, and there is no clear way to tell if your activities are legal in the country where you are using the scraper.
However, it is not scraping itself that carries the greatest risk. Most risk is in using the results of scraping. In particular, if you use a scraper to collect and analyze data within your systems (watch competitor prices, target audience search, e-mail collection, etc.), it is very likely that you will not have a problem with the law. If you plan to use a scraper to collect data about products and then place those products on your site (including pictures), you could potentially have problems under certain circumstances.
For our part, we believe that data scraping cannot be illegal. Just because any program to automate something cannot be illegal. We are convinced that in the next few years a legal framework for scrapbooking will be created. Based on this database, you will be able to safely use programs to automatically collect any information.
Be careful and cautious. Scraping gives you a lot of opportunities to collect data. We wish you wisdom and responsibility in making decisions in this area.
And if you suddenly decide to use our application, we will be glad to receive your questions and wishes!

